
Infertility: Everything you need to know
If you are trying to get pregnant, it’s normal to have doubts. Find out the risk factors that can affect male and female fertility.
Live well by preventing: explanations, advice and tips for your health.
75 Results

If you are trying to get pregnant, it’s normal to have doubts. Find out the risk factors that can affect male and female fertility.

It's a type of psychotherapy that can assist the entire family in facing various challenges. Discover what family therapy is and why it's important.

If ignored, fatigue can reach alarming levels. Discover the warning signs and how to treat this condition.
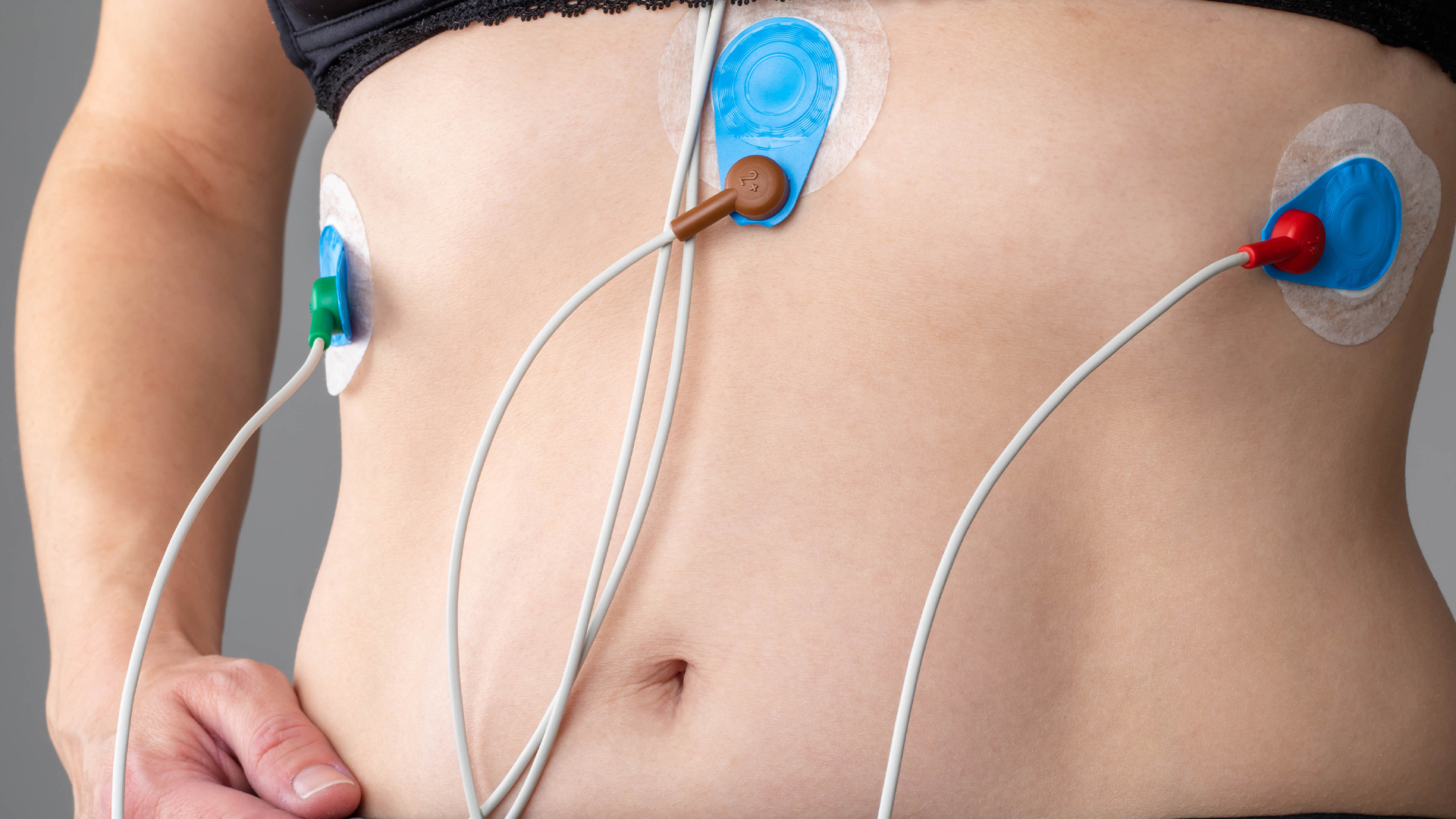
Cardiac event monitors help diagnose arrythmias early on, and can save lives. Find out how they work and what precautions to take.

Ambulatory Blood Pressure Measurement is an exam that monitors blood pressure, even during sleep. Find out how it’s done and who should do it.

Colonoscopy is extremely effective for colorectal cancer screening. Find out how it’s done, how to prepare and what risks are involved.

Endoscopy is one of the exams that causes the most anxiety, but it can be performed with sedation. Find out what it’s for, how it’s done and what precautions to take.

Clubfoot is easily treated but, if it does not receive the necessary attention, it can affect your baby’s motor skill development. Find out how this condition is identified and treated.

Discover what Aesthetic Medicine is, what it’s for and what treatments are available.

Before travelling, it’s important to take some precautions to have a safe trip. Find out what a pretravel consultation is and why you should schedule one.