
Femoroacetabular Impingement: symptoms, treatment and recovery
If left untreated, many cases of Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI) lead to the development of hip osteoarthritis. Find out what FAI is and how it is treated.
Live well by preventing: explanations, advice and tips for your health.
99 Results

If left untreated, many cases of Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI) lead to the development of hip osteoarthritis. Find out what FAI is and how it is treated.

Severe pain, reduced mobility and less quality of life. Hip arthrosis or coxarthrosis can have debilitating consequences. Find out what it is and how it’s treated.
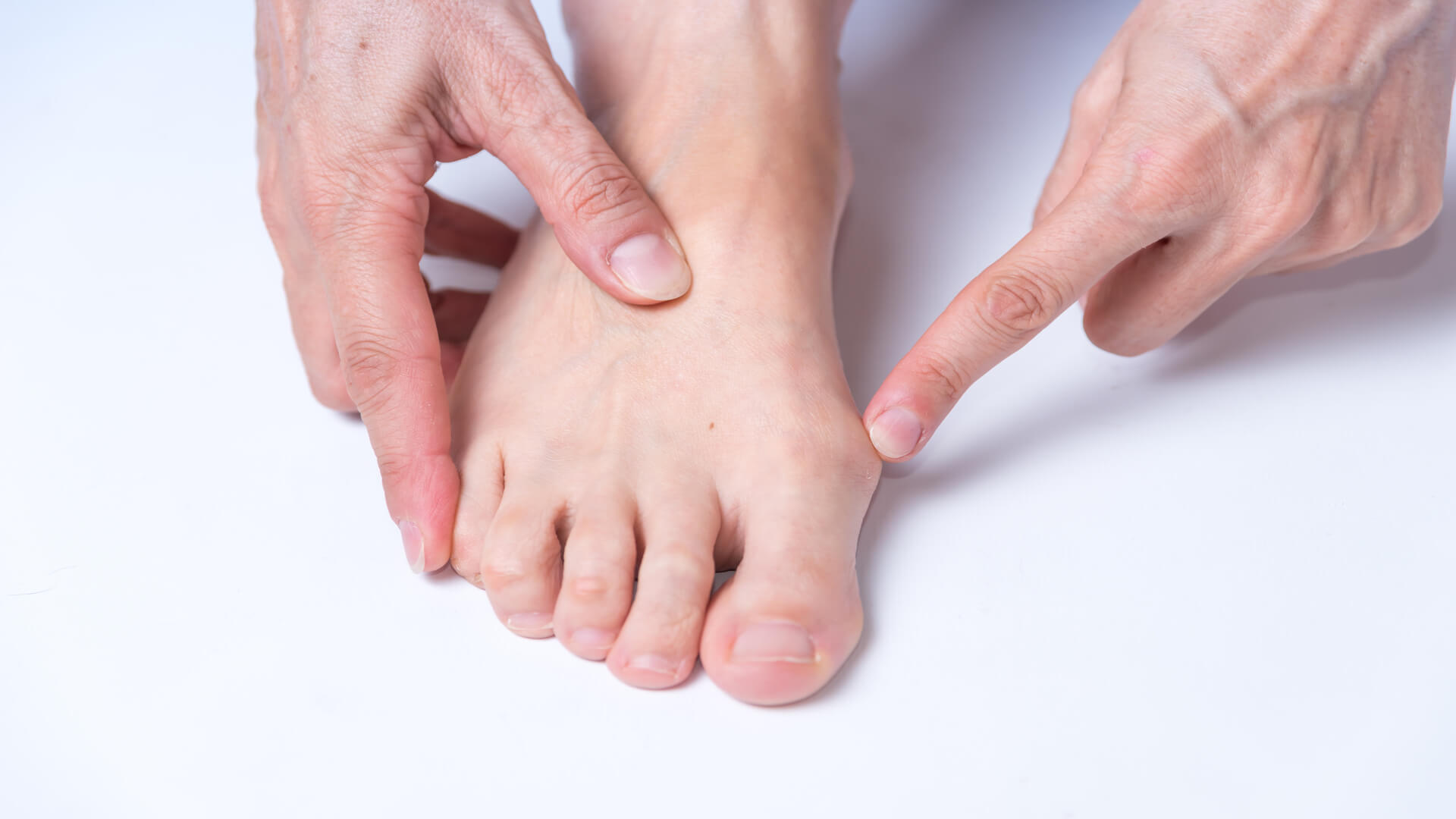
Bunions can be painful and make walking difficult. They can’t always be avoided, but there are ways to treat them. This article will clear up your doubts about bunions.
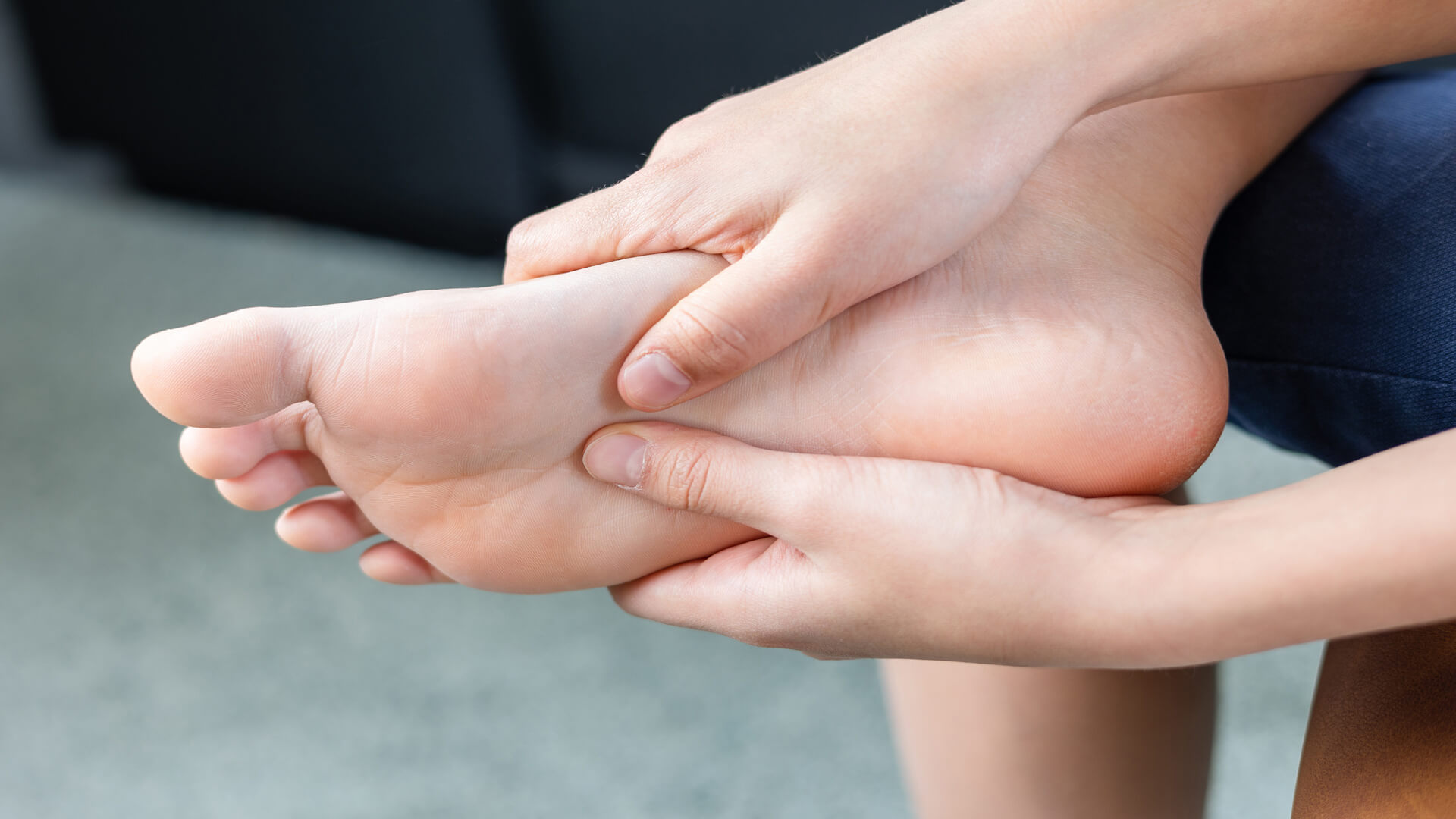

Morton’s Neuroma is a benign thickening of a nerve in the foot, normally between the 3rd and 4th toe.
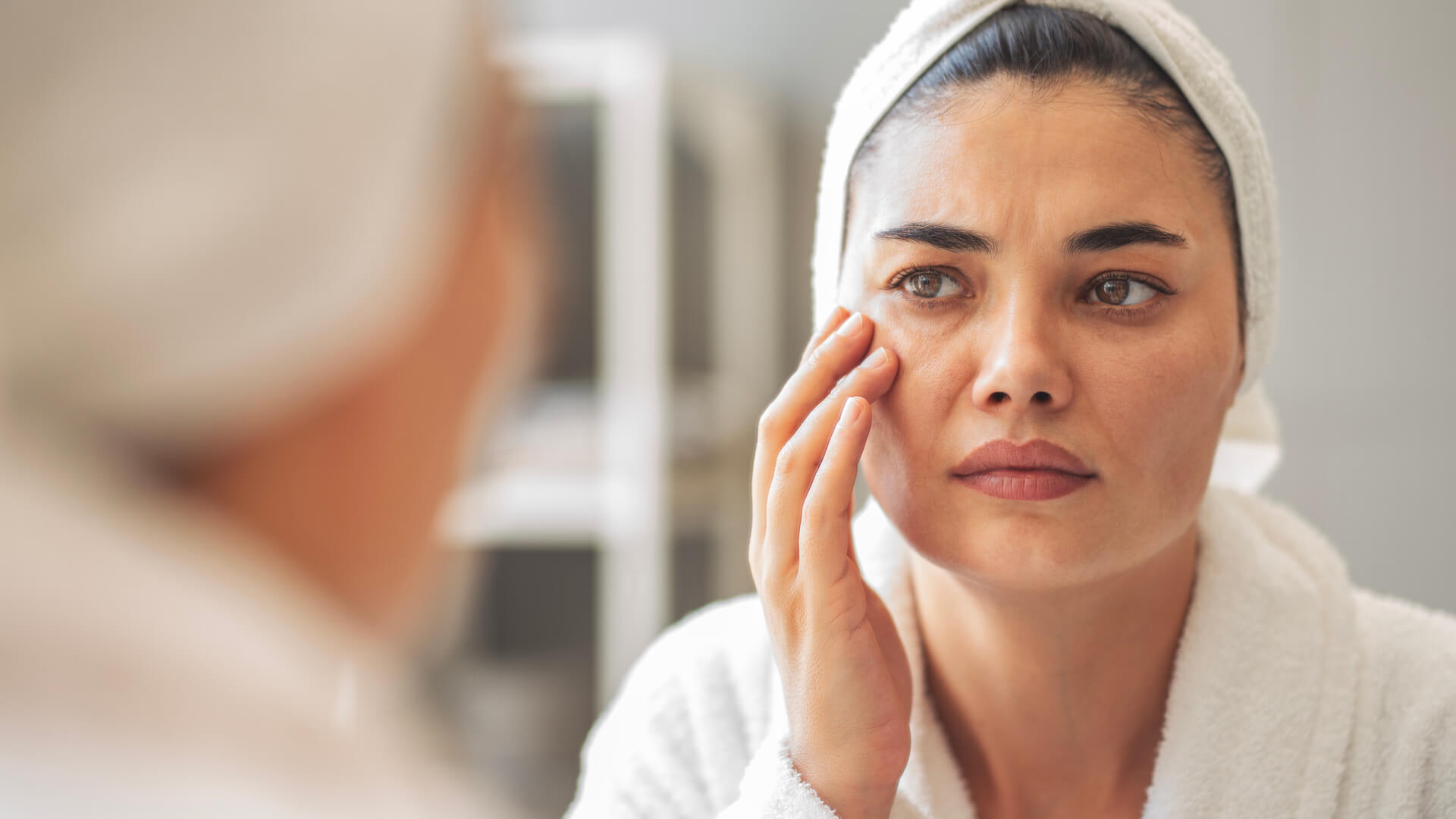

Find out more about injectable hyaluronic acid, how it works, the principal benefits, precautions to take after the procedure and expected results.
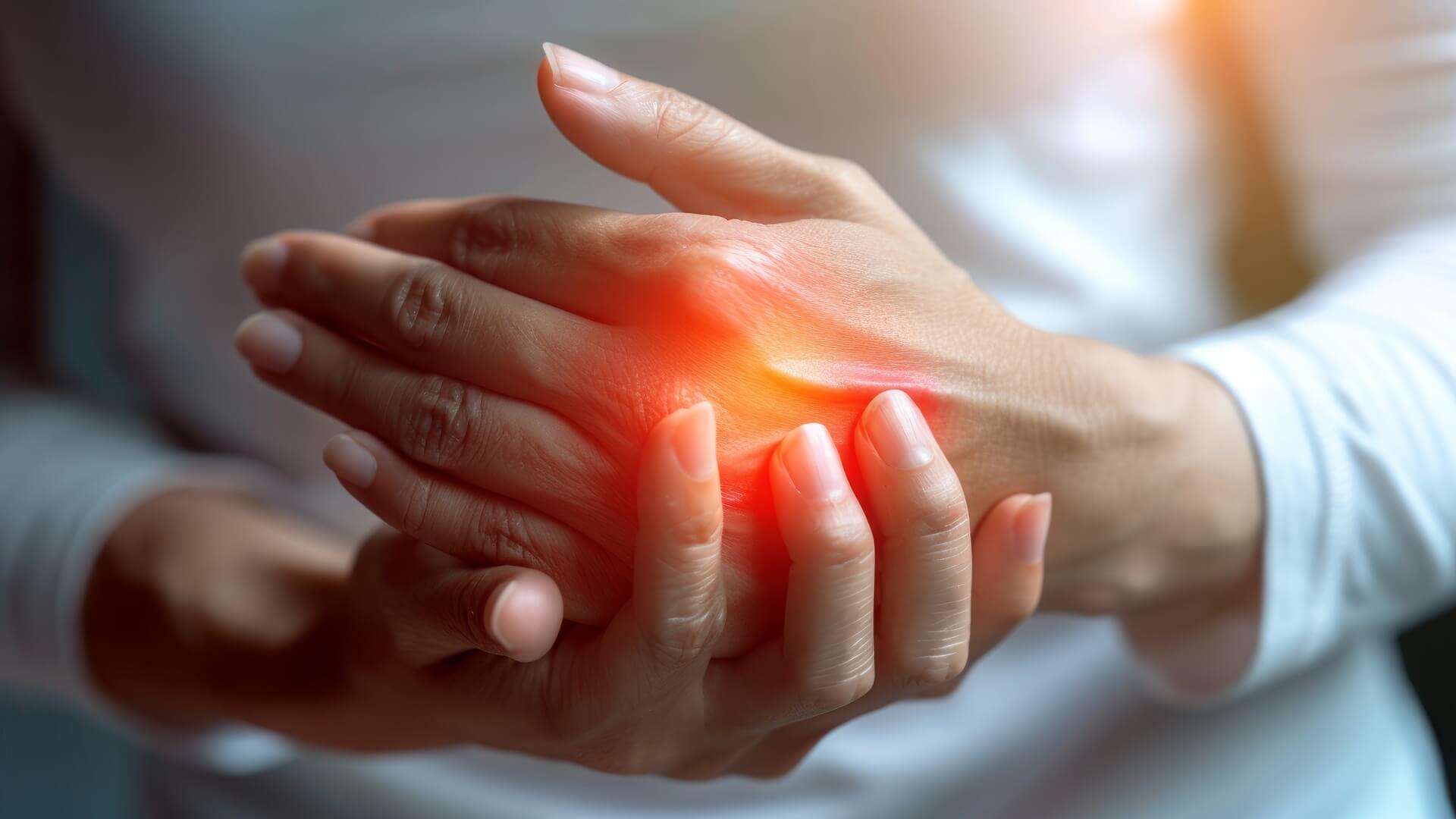

These are the 3 principal hand disorders that cause great suffering and loss of independence. Discover the symptoms and how to treat them.
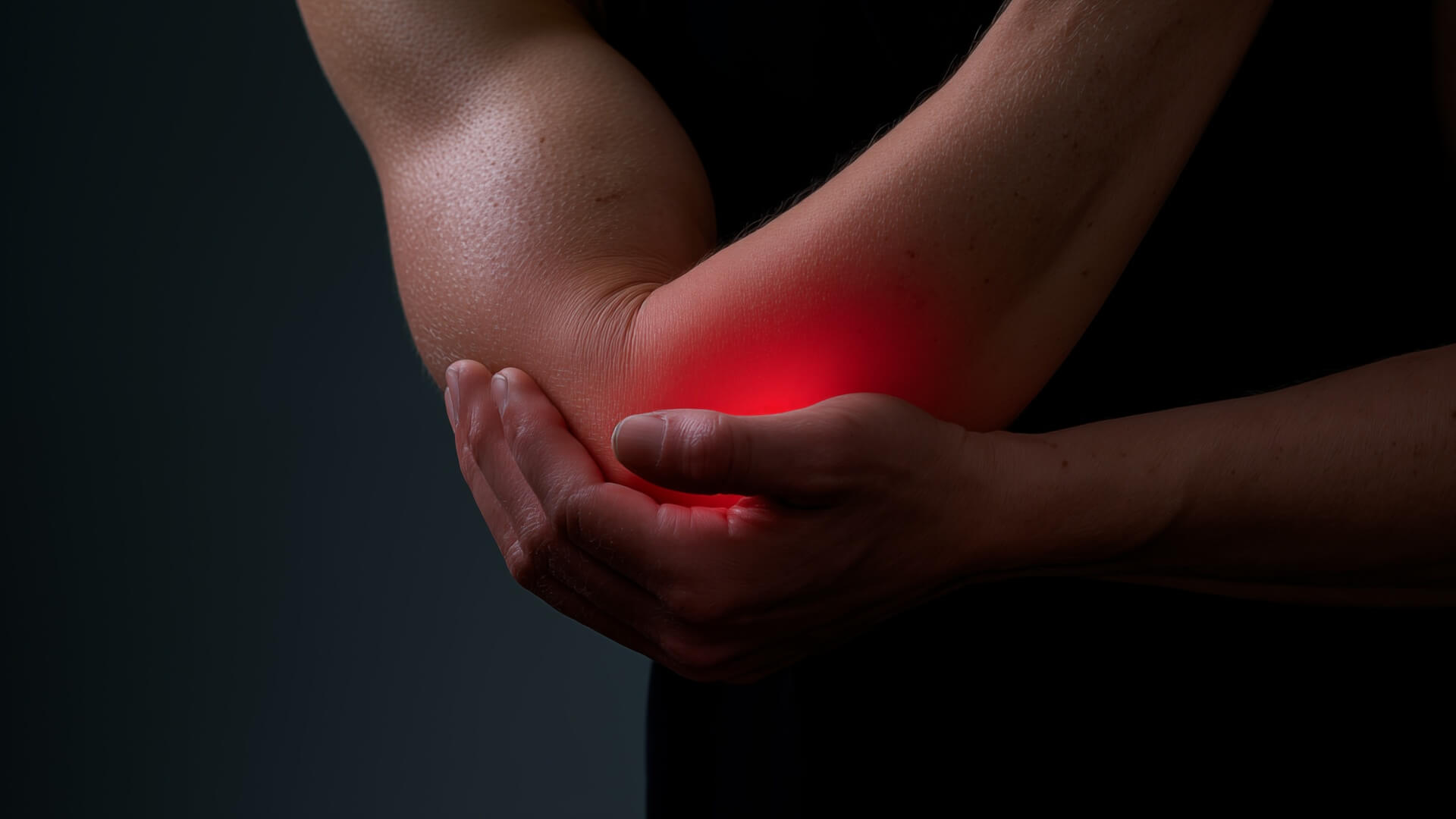
Tendinopathy is one of the most common and debilitating health problems today. Find out what this condition is, the symptoms to look out for and how it’s treated.
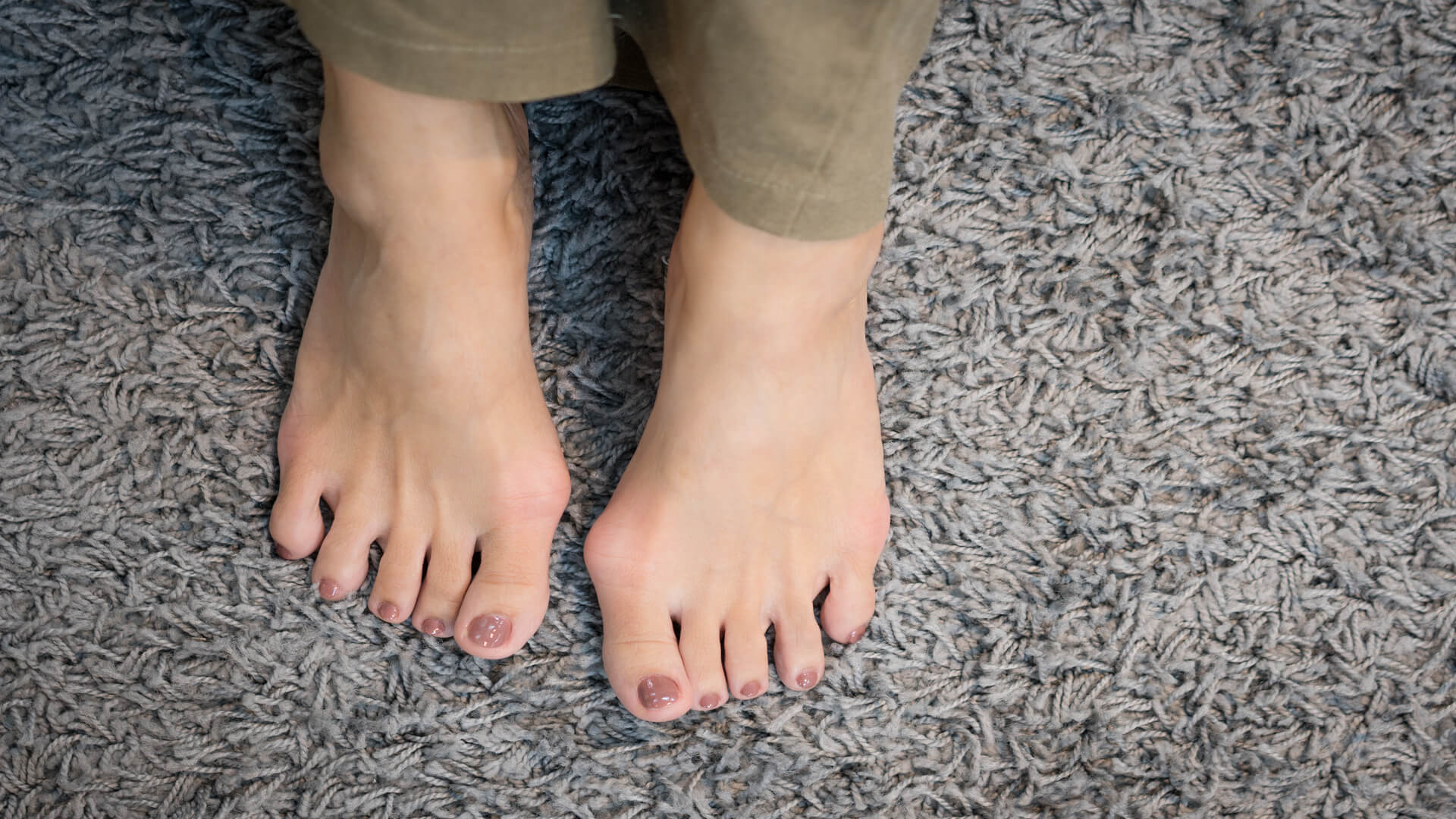

Toe deformities are quite common and can be treated effectively. Find out how.
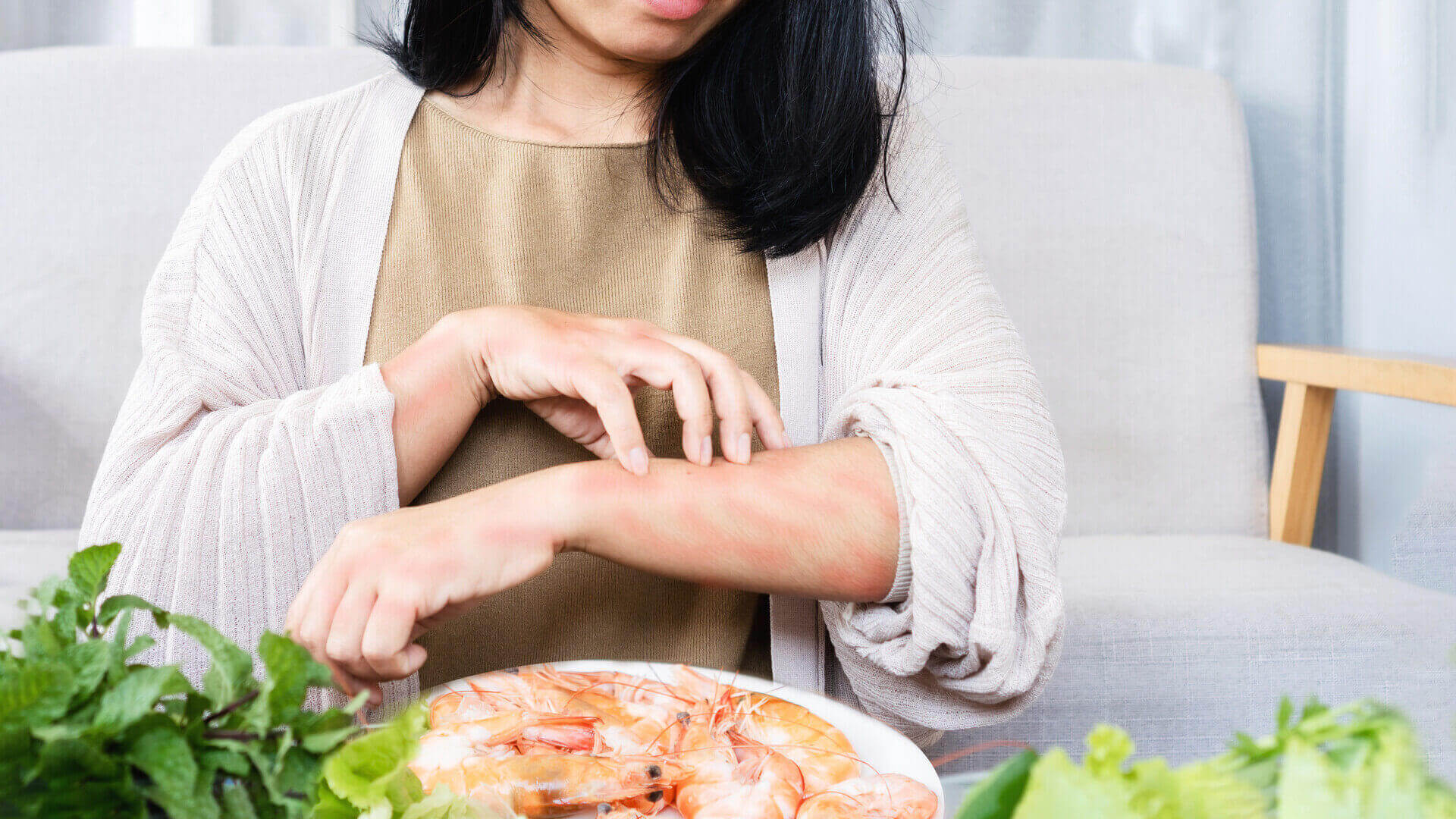

In some cases, a food allergy can be a serious health risk. With a correct diagnosis and the right medical care, you can control the condition and avoid complications. Find out how to take action and protect yourself.
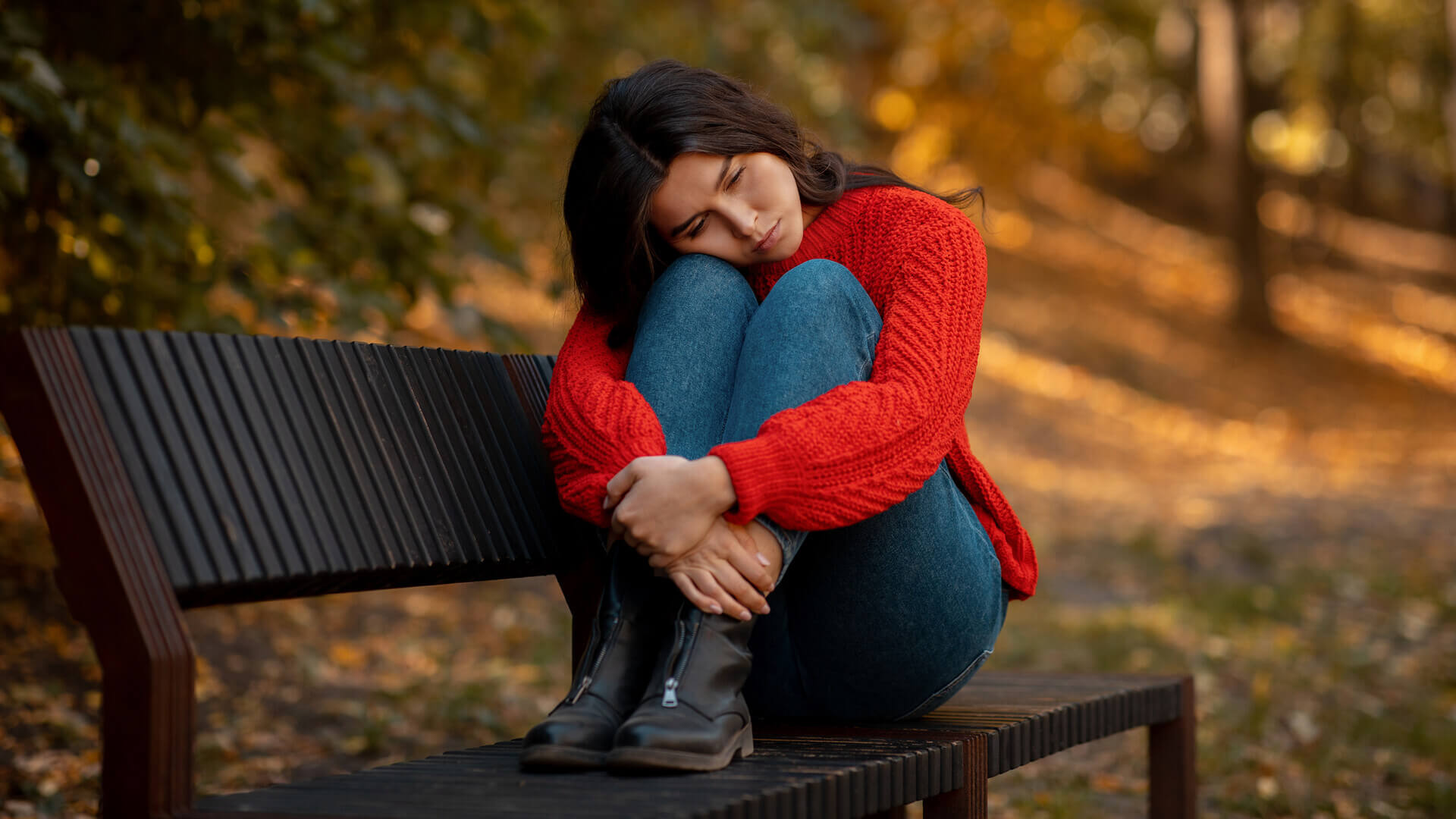

Find out what seasonal affective disorder is, as well as the symptoms, causes and treatment options. Also learn how to recognise the most common signs in autumn and winter, and when you should seek medical help.