In Portugal, approximately 10 thousand people suffer from sudden cardiac death every year. Therefore, it’s imperative to recognise the signs of problems that can impact an organ that is so vital to the whole body. Find out how tachycardia affects normal heart function, what symptoms to look out for and how it’s treated.
What is tachycardia?
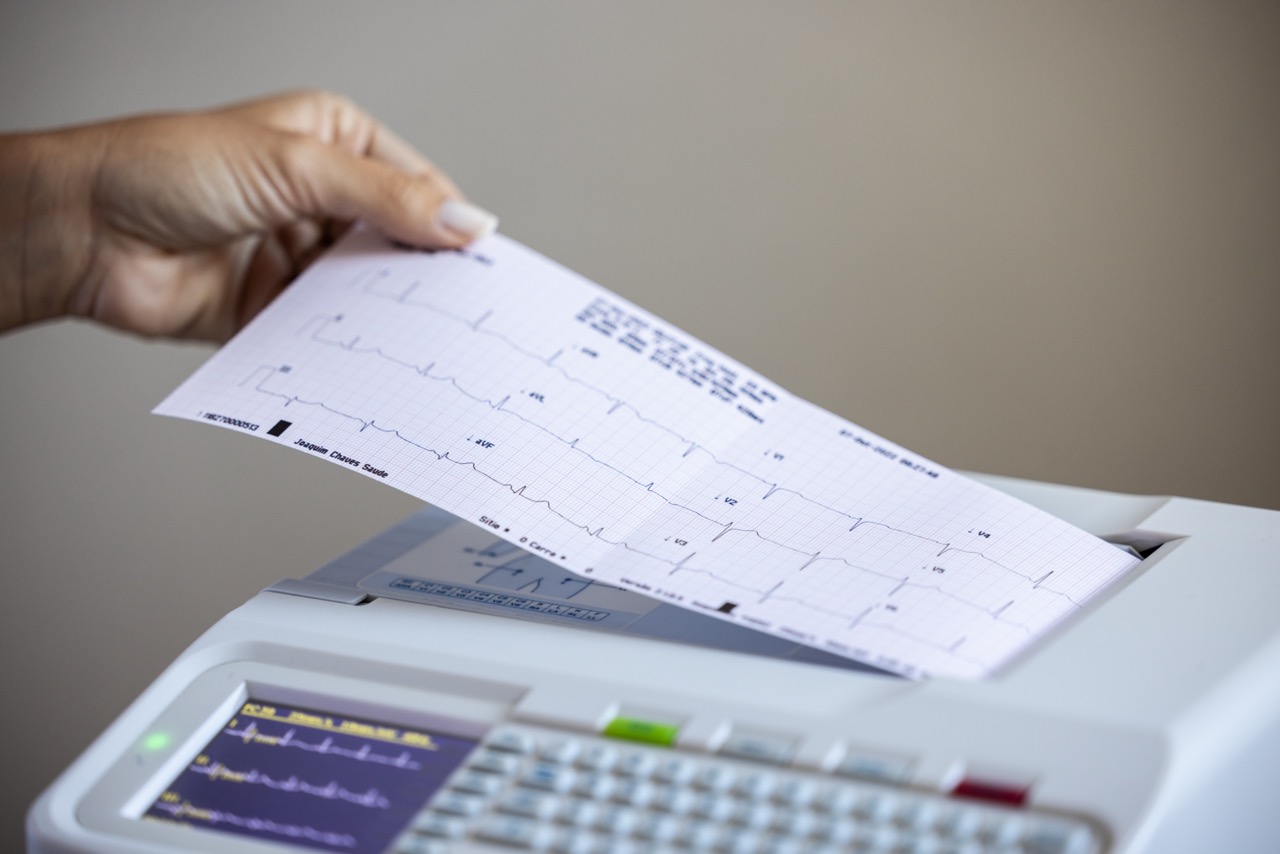
Tachycardia is the increase in heart rate above 100 beats per minute (BPM). A normal heart rate at rest is between 60 and 100 BPM, but this varies greatly from person to person, depending on exertion, emotional state and age.
However, an increase in heart rate doesn’t always imply a tachycardia diagnosis. The heart is expected to beat faster during intense physical activity, returning to normal after the person rests. This diagnosis is made when the heart rate exceeds 100 BPM with the person at rest.
The number of heartbeats can be counted by palpating the arterial pulse or using readily available devices that monitor heart rate. In addition, it is also important to determine whether the heartbeat is regular or irregular.
The most severe type of tachycardia is called atrial fibrillation, which accounts for around 15% of strokes (cerebrovascular accidents). This occurs when the heart beats rapidly and irregularly, more often with an elevated heart rate, making this one of the most common types of tachycardia. As a result, the heart is unable to pump blood effectively, thus depriving tissues of oxygen.
What are the principal symptoms of tachycardia?
The symptoms of tachycardia result from a decrease in oxygen supply to the human body. We highlight the following:
- Feeling a rapid heartbeat, even at rest (palpitations).
- Dizziness or lightheadedness.
- Shortness of breath.
- Chest pain.
- Fatigue.
- Fainting.
If you experience these symptoms, you should consult your cardiologist to identify the cause. Some types of tachycardia may be associated with blood clot formation (which can cause stroke), myocardial infarction (heart attack), heart failure or even sudden death. Therefore, do not hesitate to seek specialised help.
What can cause tachycardia?
Tachycardia can be both a symptom of another condition and a disorder in itself. Some medical conditions such as heart and lung disease, anaemia, fever, atherosclerosis or thyroid disorders can cause an abnormal heartbeat. In these cases, it’s urgent to seek medical assistance.
On the other hand, this can also be the body’s response to certain everyday situations, such as:
- Intense pain;
- Stress or anxiety;
- Panic attacks or phobias;
- Intense physical exercise;
- Strong emotions, such as fear, happiness or intense fright;
- Tea, coffee, alcohol, energy drinks, chocolate or tobacco consumption;
- Use of certain medications.
However, in these commonplace circumstances, if the heart rate does not return to normal (for example, after completing physical exercise or when the body eliminates the substances present in alcohol or coffee), then this is a situation that requires medical attention. Sometimes the cause remains unknown, but age and a family history of tachycardia or heart disease may be risk factors.
How to treat tachycardia?
The most effective way to treat tachycardia is prevention. Reduce the risk by maintaining healthy lifestyle habits, such as exercising regularly, eating a balanced diet and maintaining a healthy weight. If heart disease is already present, this should be monitored and treated correctly. It’s essential to control blood pressure and cholesterol levels through regular medical check-ups, while also avoiding unhealthy habits like smoking, alcohol, excessive coffee and stress. This will provide better control of any underlying conditions that may be causing tachycardia.
When necessary, the therapeutic strategy aims to lower the heart rate, prevent future episodes and minimise associated complications. Treatment can vary according to the type of tachycardia. This may involve using medications or introducing medical devices that detect and correct dangerously fast and/or slow heart rates, such as a pacemaker or defibrillator. In serious cases, surgery may be required, such as bypass surgery or heart valve reconstruction/replacement. At Joaquim Chaves Saúde, your cardiologist will determine the best therapeutic approach for your case and discuss necessary lifestyle changes with you.